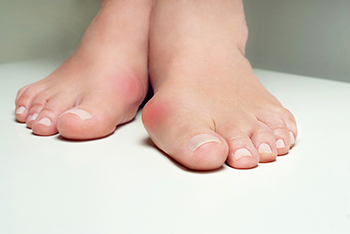
A bunion is a painful bony lump that forms at the base of the big toe when the top of the toe leans toward the second toe. Bunions often develop due to inherited foot structure, injuries, or excessive pressure on the front of the foot. People with flat feet or inward-rolling ankles may be more prone to the formation of bunions, as these conditions affect weight distribution and joint stability. Wearing tight, narrow, or high-heeled shoes can worsen the problem by increasing pressure on the big toe joint. Certain types of arthritis, like rheumatoid arthritis or gout, may also contribute by weakening the joint over time. As a bunion progresses, symptoms can include pain, redness, swelling, stiffness, and difficulty wearing shoes comfortably. Some people also develop corns, calluses, or ingrown toenails due to toe crowding. A podiatrist can evaluate the severity of a bunion and discuss treatment options, including footwear modifications or surgery if the condition significantly affects mobility. If you have foot problems related to bunions, it is suggested that you schedule an appointment with a podiatrist for a diagnosis and treatment options.
If you are suffering from bunion pain, contact Jennifer Swan, DPM of Right Step Foot Care. Our doctor can provide the care you need to keep you pain-free and on your feet.
What Is a Bunion?
Bunions are painful bony bumps that usually develop on the inside of the foot at the joint of the big toe. As the deformity increases over time, it may become painful to walk and wear shoes. Women are more likely to exacerbate existing bunions since they often wear tight, narrow shoes that shift their toes together. Bunion pain can be relieved by wearing wider shoes with enough room for the toes.
Causes
- Genetics – some people inherit feet that are more prone to bunion development
- Inflammatory Conditions - rheumatoid arthritis and polio may cause bunion development
Symptoms
- Redness and inflammation
- Pain and tenderness
- Callus or corns on the bump
- Restricted motion in the big toe
In order to diagnose your bunion, your podiatrist may ask about your medical history, symptoms, and general health. Your doctor might also order an x-ray to take a closer look at your feet. Nonsurgical treatment options include orthotics, padding, icing, changes in footwear, and medication. If nonsurgical treatments don’t alleviate your bunion pain, surgery may be necessary.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact our office located in Westerville, OH . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.
